Путь на сайте
НАЦИОНАЛЬНАЯ РАМКА КВАЛИФИКАЦИЙ
- Details
- Category: Без категории
- Published on Friday, 19 February 2021 10:44
- Written by Макаревич Евгения
- Hits: 24765
Постановление КМУ № 1341 «Об утверждении Национальной рамки квалификаций» от 23 ноября 2011
НАЦІОНАЛЬНА РАМКА КВАЛІФІКАЦІЙ
- Details
- Category: Без категории
- Published on Thursday, 18 February 2021 08:07
- Written by Super User
- Hits: 51394
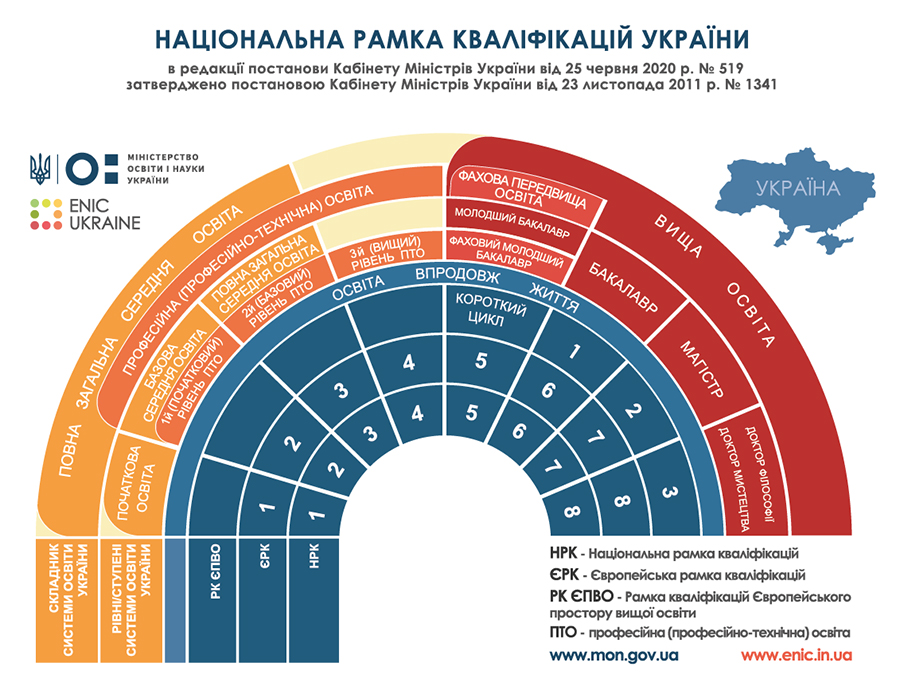
Постанова КМУ № 1341 «Про затвердження Національної рамки кваліфікацій» від 23 листопада 2011>>
Полезные ссылки
- Details
- Category: Без категории
- Published on Monday, 25 November 2019 11:10
- Written by Макаревич Евгения
- Hits: 142101
Министерство образования и науки Украины
Единая государственная электронная база по вопросам образования
Украинский государственный центр международного образования
Национальное агентство по обеспечению качества высшего образования
Useful Links
- Details
- Category: Без категории
- Published on Monday, 25 November 2019 16:56
- Written by Макаревич Евгения
- Hits: 14169
Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine
The Unified State Electronic Database on Education
State Enterprise "Ukrainian State Centre for International Education"
National Agency for Higher Education Quality Assurance (NAQA)
The page of Ukraine on the EHEA (European Higher Education Area) website
SERVICES AND CONTACT INFORMATION
- Details
- Category: Без категории
- Published on Friday, 15 September 2017 13:23
- Hits: 36378
You may contact a specialist of the National Information Centre of Academic Mobility and receive information and explanations regarding the system of education in Ukraine at:
25, V. Chornovola, Kyiv, 01135, Ukraine
Tel.: +38 044 484 64 25
E-mail: info@enic.in.ua
www.enic.in.ua
Other organizational units of the Centre:
Apostilization of Ukrainian education-confirming documents:
Тel.: +38 044 484 64 45, +38 044 484 64 95
Fax: +38 044 486 23 29
E-mail: centre@apostille.in.ua
www.apostille.in.ua
Recognition of foreign qualifications:
Тel.: +38 044 486 20 43, +38 044 486 25 43
Fax: +38 044 486 18 29
E-mail: centre@naric.in.ua
www.naric.in.ua
More Articles...
- Description of Documents on Higher Education (Research Degrees), Supplements thereto, Academic Transcripts of State Standard
- Швеция приглашает на конференцию 12-13 июня 2017 г.
- EDUCATIONAL DOCUMENTS IN UKRAINE
- ДОКУМЕНТЫ О ПОСЛЕДИПЛОМНОМ ОБРАЗОВАНИИ
- Описание документов о высшем образовании (научные степени) государственного образца и приложений к ним, академической справки
- ДОКУМЕНТЫ О СРЕДНЕМ ОБРАЗОВАНИИ
- Documents on Basic Secondary Education
- Transcript of records
- Diploma supplement
- Supplement
- Foreign students’ diploma
- PhD and candidate of sciences diploma
- Master diploma
- Specialist diploma
- Bachelor diploma
- Qualified Worker’s Diploma
- Junior specialist diploma
- Documents on Completed Secondary Education
- EDUCATION SYSTEM
- HIGHER EDUCATION STRUCTURE





